
Liquid level sensors, also known as level switches, are designed to change state when immersed in a liquid. They are used to determine if a specific level of liquid or oil is present in a container.
What are the different types of level sensors?
Different types of liquid level sensors include
1. Optical
2. Capacitive
3. Conductive
4. Diaphragm
5. Floating
1. Optical Level Sensors
Optical sensors work on a solid-state principle. They use an infrared LED and a phototransistor, which are optically coupled when the sensor is in air. When the sensing tip is immersed in a liquid, infrared light escapes, changing the output state. These sensors can detect the presence or absence of almost any liquid. They are insensitive to ambient light, unaffected by foam when in air, and unaffected by small bubbles when in liquid. This makes them useful in situations where changes in state must be noticed quickly and reliably, and where they must operate reliably for long periods of time without maintenance.
The disadvantage of an optical level sensor is that it can only determine if a liquid is present. If variable levels are required (25%, 50%, 100%, etc.), additional sensors are required for each level.
2. Capacitive Level Sensors
A capacitive level switch uses 2 conductive electrodes (usually made of metal) placed a short distance apart from each other in a circuit. When the electrodes are immersed in the liquid, the circuit is completed.
The advantage of a capacitive level switch is that it can be used to determine the rise or fall of liquid in a container. By making the electrodes the same height as the container, the capacitance between the electrodes can be measured. No capacitance means no liquid. Full capacitance means the container is full. The "empty" and "full" measurements must be recorded, and then the level is displayed with a meter calibrated at 0% and 100%.
While capacitive level sensors have the advantage of no moving parts, one of their disadvantages is that corrosion of the electrodes will change the capacitance of the electrodes, requiring cleaning or recalibration. They are also more sensitive to the type of liquid used.
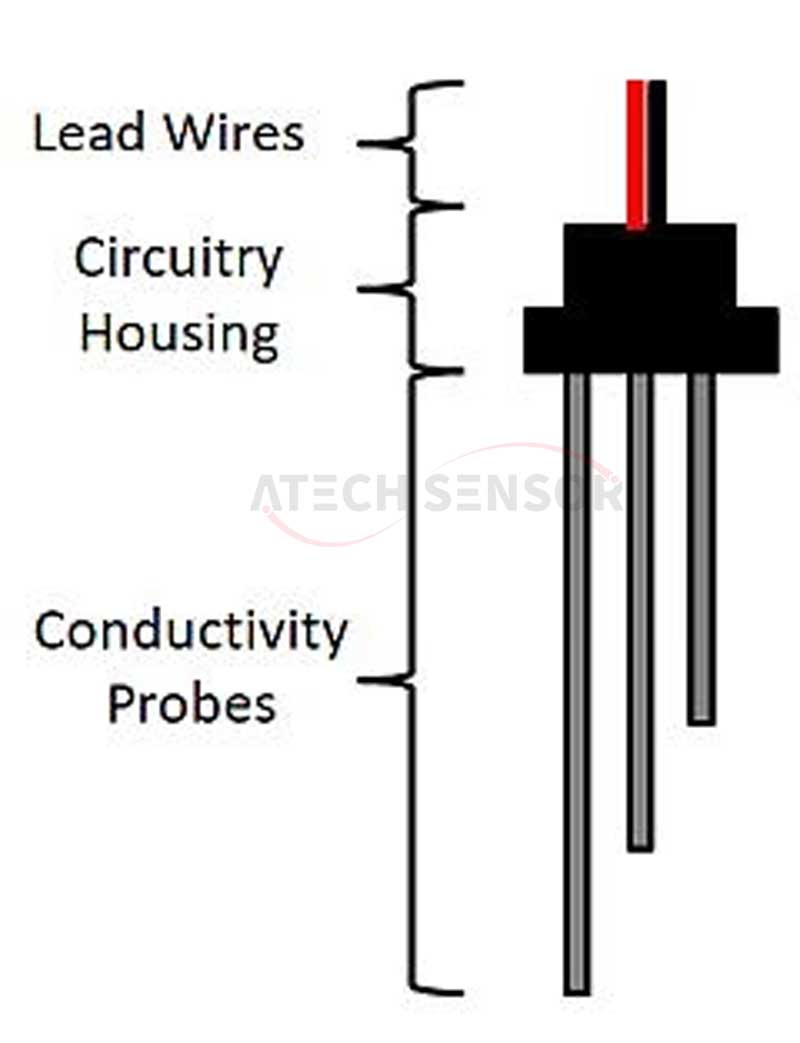
3. Conductive Level Sensor
A conductive level switch is a sensor that has electrical contacts at specific liquid levels. Two or more insulated electrodes with exposed tips are used inside a pipe inserted into the liquid. The longer electrode carries a low voltage, while the shorter electrode is used to complete the circuit when the liquid level rises to equal it.
Like capacitive level switches, conductive level switches also depend on the conductivity of the liquid. Therefore, they are only suitable for measuring certain types of liquids. In addition, these sensor tips must be cleaned regularly to reduce dirt.
4. Diaphragm Level Sensors
Diaphragm or pneumatic level switches rely on air pressure to push a diaphragm, which engages a microswitch inside the body of the device. As the liquid level rises, the internal pressure inside the sensing tube increases until the microswitch or pressure sensor is activated. As the liquid level drops, the air pressure also drops and the switch disengages.
The advantages of a diaphragm level switch are that it does not require a power source to be installed inside the tank, can be used with a wide range of liquids, and the switch does not come into contact with the liquid. However, since it is a mechanical device, it will require maintenance over time.
5. Float Level Sensors
Float switches are the original level sensors. They are mechanical devices. A hollow float is attached to an arm. As the float rises and falls in the liquid, the arm is pushed up and down. The arm can be attached to a magnetic or mechanical switch to determine on/off, or to a meter that rises from full to empty as the level drops.

The float switch in a toilet tank is the most commonly used float level sensor. Sump pumps also use float switches (see photo at right), and they are a cost-effective way to measure water levels in basement cesspools.
Float switches can measure any type of liquid and can be designed to operate without electricity. The disadvantages of float switches are that they are larger than other types of switches, and because they are mechanical, they must be maintained more frequently than other level switches.

